WHAT IS ENDOVASCULAR STENT GRAFT REPAIR?
Endovascular stent grafting is a minimally invasive surgical procedure involving the placement of an expandable stent graft within the aorta to treat an aortic disease without operating directly on the aorta. The endovascular stent graft reinforces the wall of the aorta and helps keep the damaged area from rupturing.
The procedure is performed in the cath-lab by a vascular surgeon usually assisted by an interventional cardiologist.
WHAT IS AORTIC ANEURYSM?
An aortic aneurysm is an abnormal bulge that occurs in the wall of the major blood vessel (aorta) that carries blood from your heart to your body. There are abdominal aortic aneurysms and thoracic aortic aneurysms.
The main concern is that the aneurysm might rupture. The wall of the aneurysm is weaker than a normal artery wall and may not be able to withstand the pressure of blood inside. If it ruptures then internal bleeding occurs which may be fatal.
EVAR (or endovascular aneurysm repair) refers to the stenting of abdominal aortic aneurysm. When used to treat thoracic aortic disease, the procedure is then specifically termed TEVAR for “thoracic endovascular aortic/aneurysm repair.” FEVAR (fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair) uses a stent with holes, or fenestrations, on the graft body to maintain the patency of the visceral arteries.
WHY IS ENDOVASCULAR GRAFTING OF AORTIC ANEURYSM PERFORMED?
The goals of aortic aneurysm treatment are to reduce the risk of complications from aneurysms. The major risk for untreated aneurysms is rupture, and as an aneurysm gets bigger, the risk gets greater. There are several factors to consider when deciding to treat an aneurysm with surgery, including:
- The presence of symptoms, including abdominal pain, back pain or pain in the groin or inner thigh;
- The size of the aneurysm, in particular its diameter (5,5 centimetres or more in size);
- How fast the aneurysm is growing, in particular, rapid aneurysm growth (diameter grows more than 1 centimetre per year);
- The development of an aortic dissection, which can be accompanied by sudden and severe sharp tearing pain in the chest or back;
- The patient’s overall medical condition.
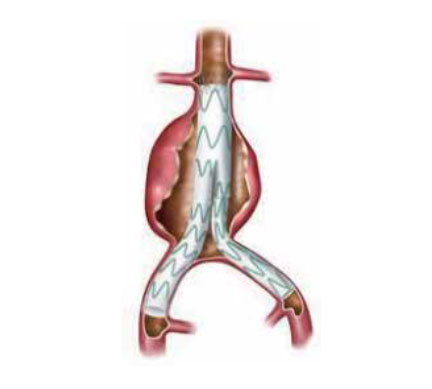
WHAT IS AORTIC DISSECTION?
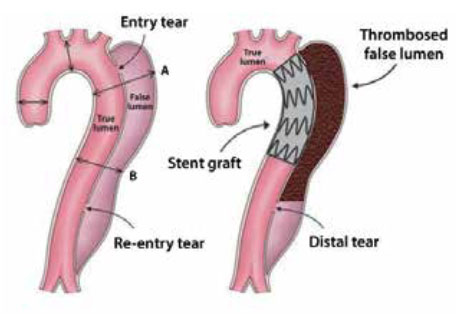
Aortic dissection occurs when a tear develops in the inner layer of the aorta. When this occurs, the aorta then bleeds into itself through the middle layer, extending this tear and leads to a separation of the layers of the aorta – known as aortic dissection. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of severe chest or back pain, often described as “tearing” in character.
Type B dissection involves a tear in the descending part of the aorta that may extend into the abdomen, complications may include mesenteric and renal ischemia, leg ischemia, paraplegia, rupture, and retrograde aortic dissection.
WHY IS ENDOVASCULAR GRAFTING OF AORTIC DISSECTION PERFORMED?
Endovascular treatment of type B aortic dissections is necessary in complicated and cases that are characterised by persistent pain, presence of visceral or limb ischemia syndrome, uncontrolled hypertension and aortic dilatation.
It is also now recommended even in the absence of initial complications because it has long-term prognostic benefits.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN ENDOVASCULAR AND OPEN SURGERY?
Unlike open surgery, which involves a long cut in your abdomen or your thorax, endovascular surgery requires only two small incisions in the area of your groin. In many cases, the surgery takes 2 to 3 hours to complete, which is much shorter than open surgery repair (that can last often 8 hours or more)
Endovascular stent grafting and open surgery grafting are both done to prevent an abdominal or a thoracic aortic aneurysm from rupturing or to treat an aortic dissection. The difference is that the endovascular stent graft is put into place inside the aneurysm or before the aorta tear in case of dissection, without removing any tissue from your aorta, and it does not require open-abdominal or open-chest surgery.
Because it is less invasive than open surgery, the recovery time for endovascular stent grafting is usually faster. Most of the time, the patient can return home within a week and return to normal activities in 4 to 6 weeks.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS OF THE PROCEDURE?
Endovascular stent grafting is a very safe procedure, safer than a conventional open abdominal or open-chest surgery.
Complications that can happen after endovascular stent grafting repair include leaking of blood around the graft, the graft moving away from its initial placement and the stent breaking. Complications that are rare include paralysis, kidney injury, large bruise where the catheter has been inserted, and infection.
WHAT HAPPENS DURING THE PROCEDURE?
You will either receive a sedative and a local anaesthesia or a general anaesthesia (to be put to sleep). You surgeon will do the procedure by percutaneous puncture or make small incisions in your groin and perform the surgery through those openings. Catheters are inserted in the incisions to guide and deliver a stent-graft through the blood vessels to the aneurysm or the dissection area. An endovascular stent graft is a fabric tube supported by metal wire stents that reinforces the weak spot in the aorta.
Using X-ray guidance, the surgeon places the graft in the area of the aneurysm or the dissection. The graft is then opened up inside the aorta and held in place with metal hooks and stents rather than sutures (stitches).
The procedure itself generally takes 2 to 3 hours. You will stay in the hospital a few days. Full recovery will take about a month.
ARE THERE ANY SIDE EFFECTS OF THE TREATMENT?
As with any surgical procedure, you will feel a bit tired for a few weeks. You may develop an inflammatory response as blood stops flowing through the aneurysm. The inflammation may cause a low-grade fever (temperature less than 38°C), make you feel like you have the flu, but the symptoms will go away in several days.
You will not notice the stent itself. You should notice no difference in your ability to perform daily activities, and you should be able to get back to all of your regular activities without any restrictions.
WHAT ARE THE RESULTS OF THE PROCEDURE?
Your doctor will discuss the results of the procedure with you. Endovascular stent graft repair produces very good outcomes.
You will need follow-up visits for the stent graft, but most patients live a normal life after the procedure. In general, patients who had an aneurysm or a dissection should follow a healthy lifestyle that includes a healthy diet and regular exercise.



